IT Connectivity History
1940s to 1960s - scale 1
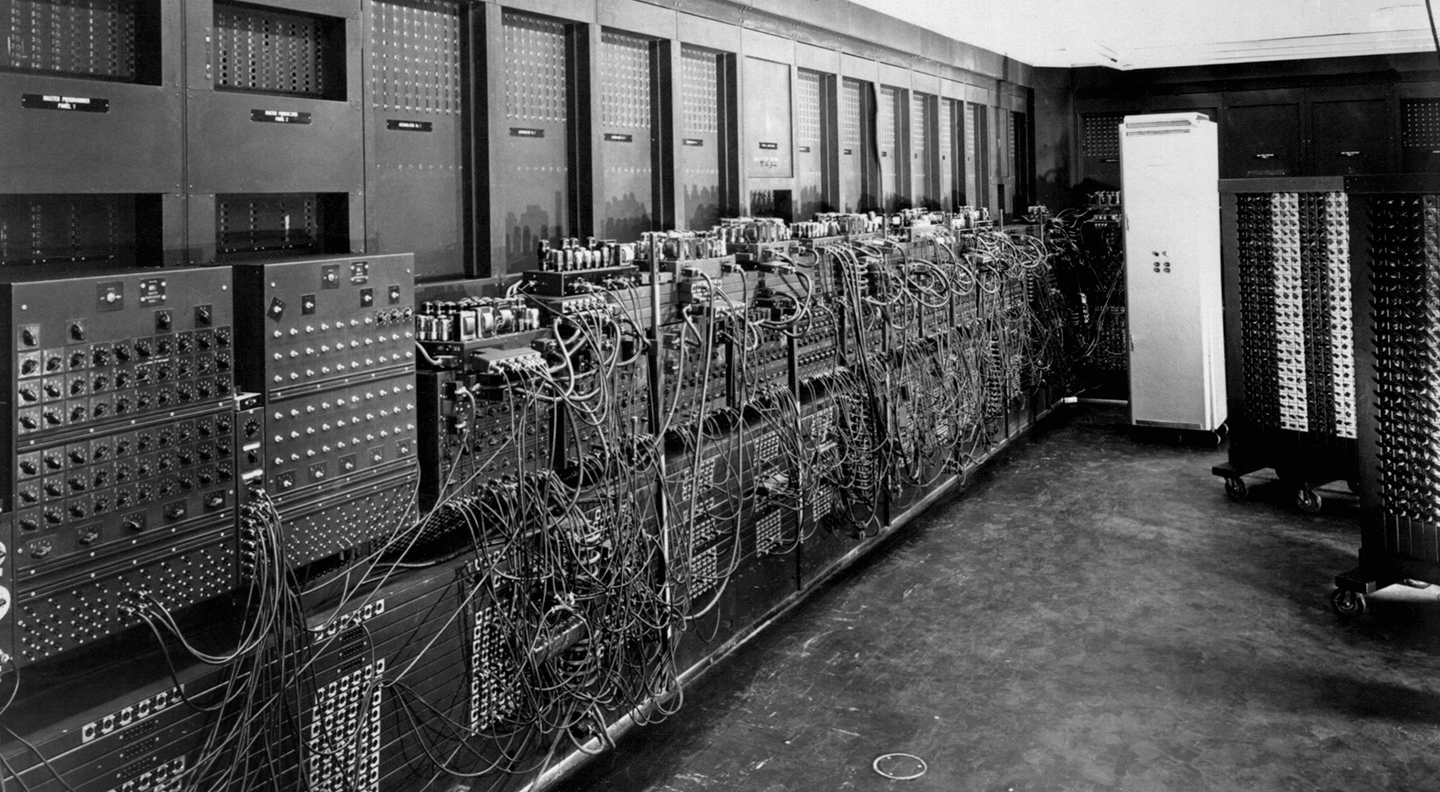
The world’s first electronic digital computer, ENIAC (electronic numerical integrator and computer), was built for the U.S. Army between 1943-1945 and ushered in the Information Age. When it was refurbished and redeployed in 1946, it was the beginning of the processes we follow in today’s IT asset disposition (ITAD) industry.
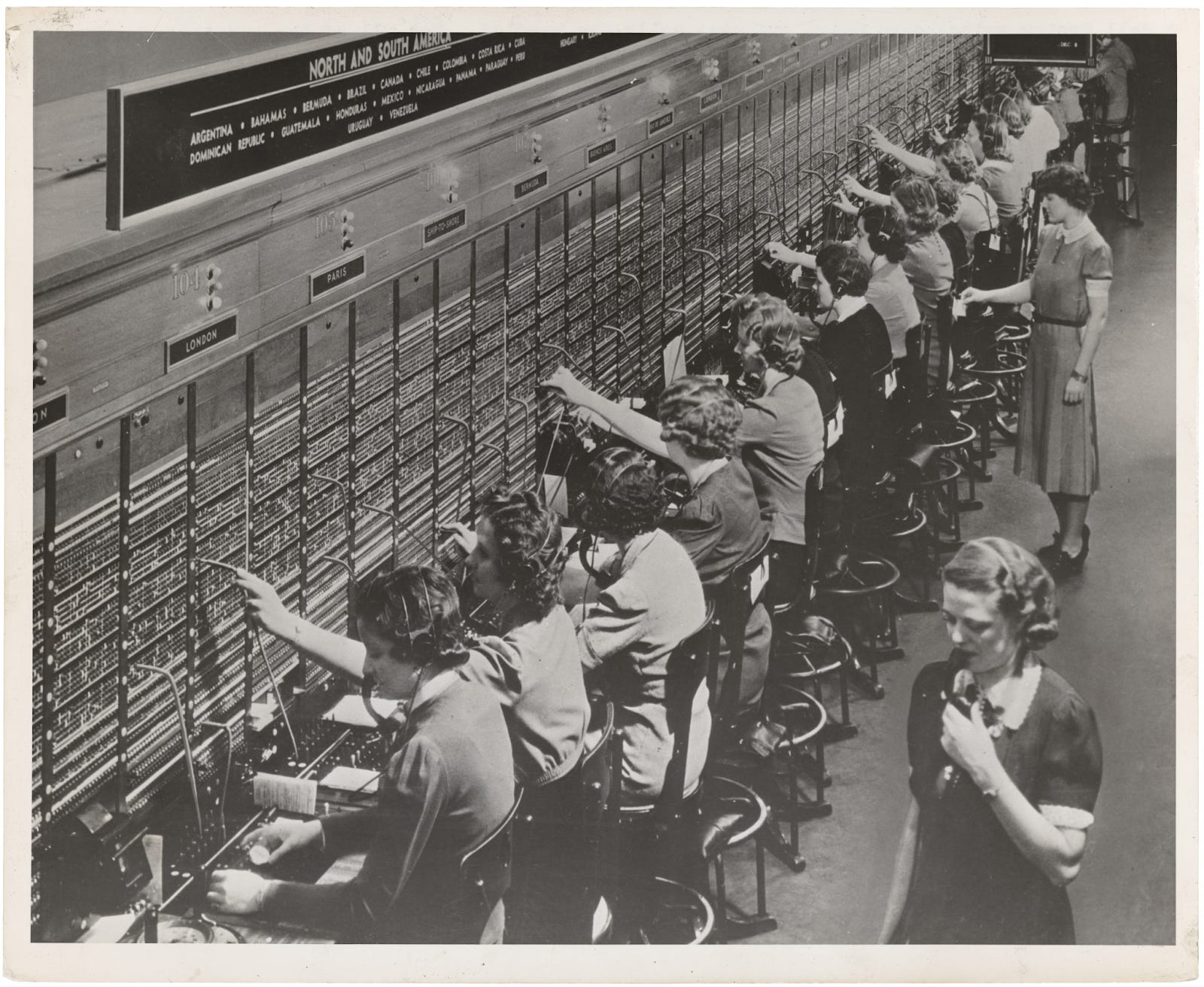
Photograph of Women Working at a Bell System Telephone Switchboard, circa 1945. (source: The U.S. National Archives on Flickr)
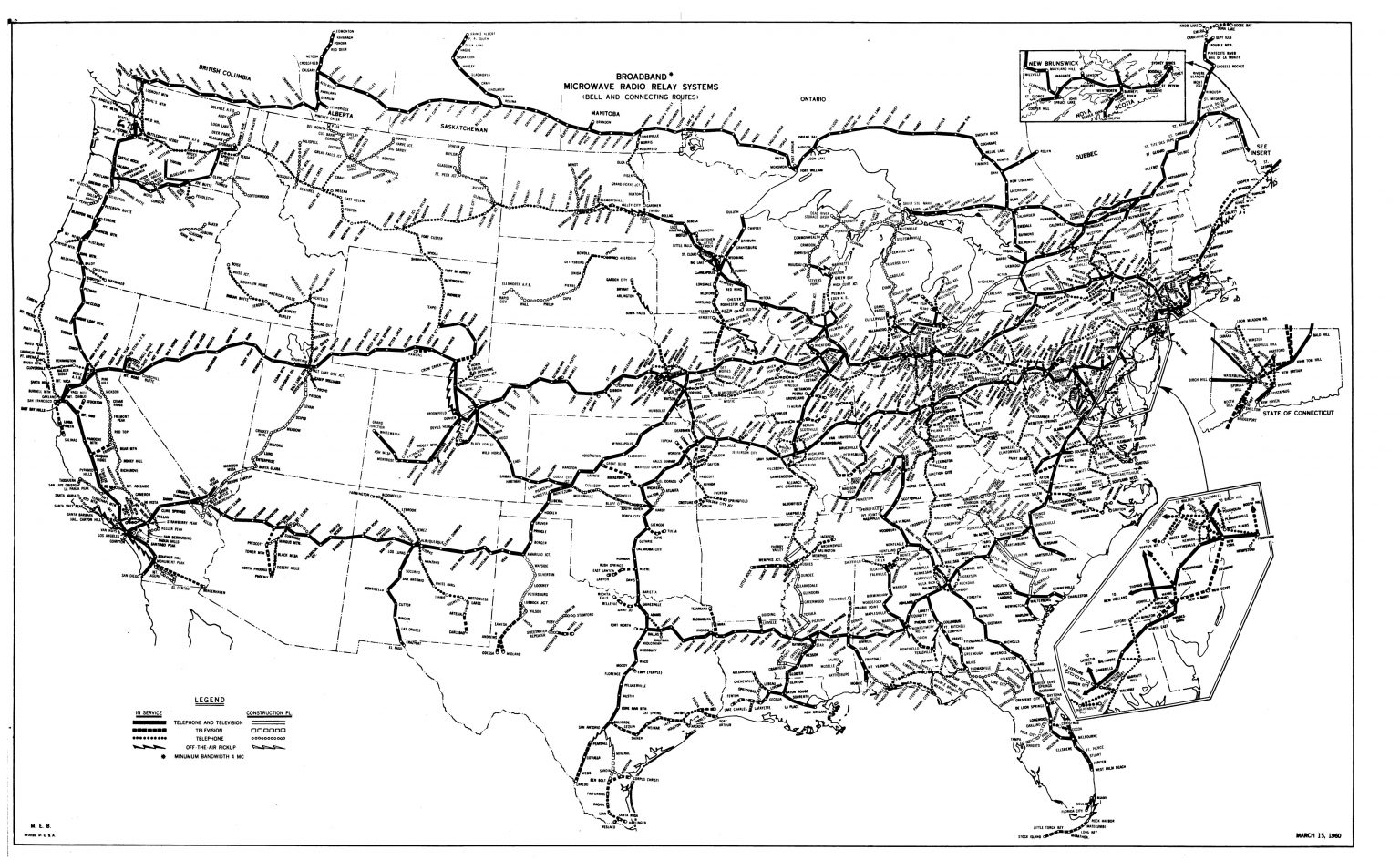
A 1960 map of the broadcast lines connecting the stations.
IBM 704 Electronic Data Processing System
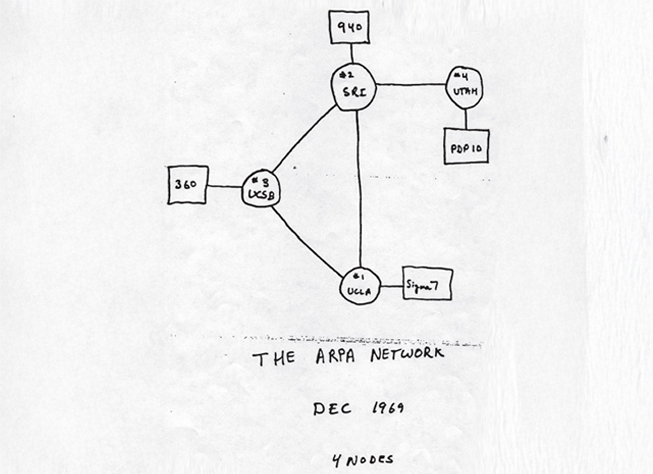
First four nodes of the ARPANET in 1969, UCSB, UCLA, UofUtah, Stanford
Early developments of the computer and its surrounding technology were fundamentally driven by the US military, or DARPA. In pressure of both WW2 and the Cold War, the government was eager to use computers for possibilities of command and control. These interests led to the development of ARPANET, the precursor to the Internet. Although the term data center has not fully emerged, computers like IBM 704 required large rooms and significant cooling capabilities, starting to resemble what we see today as data centers. Rudimentary slow communication between these computers was possible, but remained limited to the capabilities of telephone lines. Although the computers were also limited in access, programming language like BASIC were development to appeal to a larger audience during this time.
Potential Readings:
https://ed-thelen.org/comp-hist/BRL61-ibm0704.html
https://www.darpa.mil/news/features/arpanet
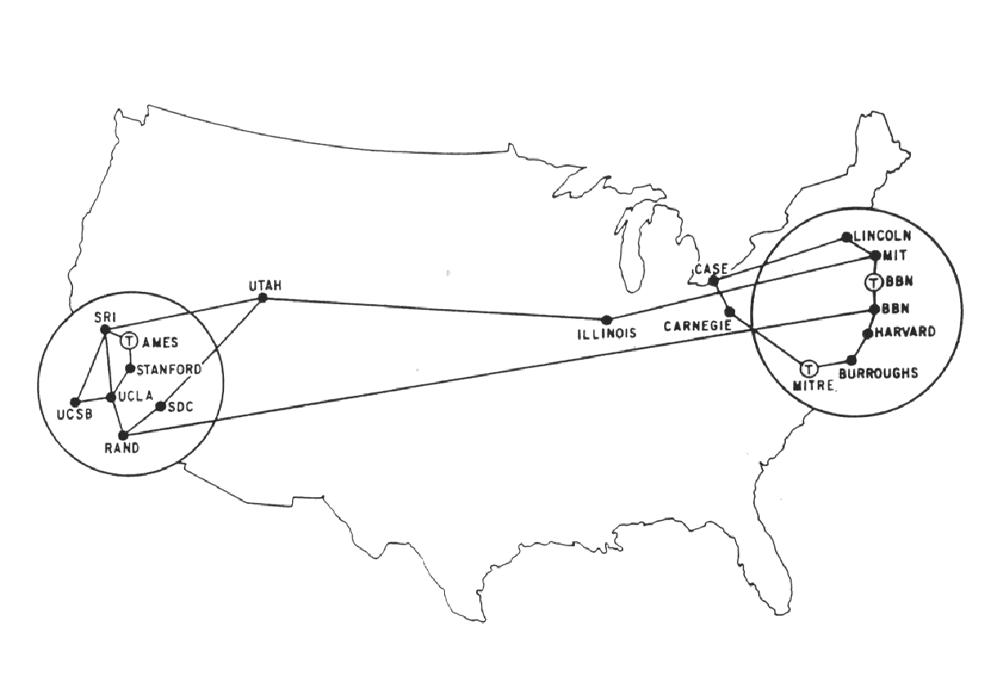
Multiple geographically dispersed nodes of ARPANET in 1970

The three computers whose makers Byte magazine referred to as the "1977 Trinity" – from left to right: the Commodore PET 2001, the Apple II, and the Tandy/Radio Shack TRS-80 Model 1
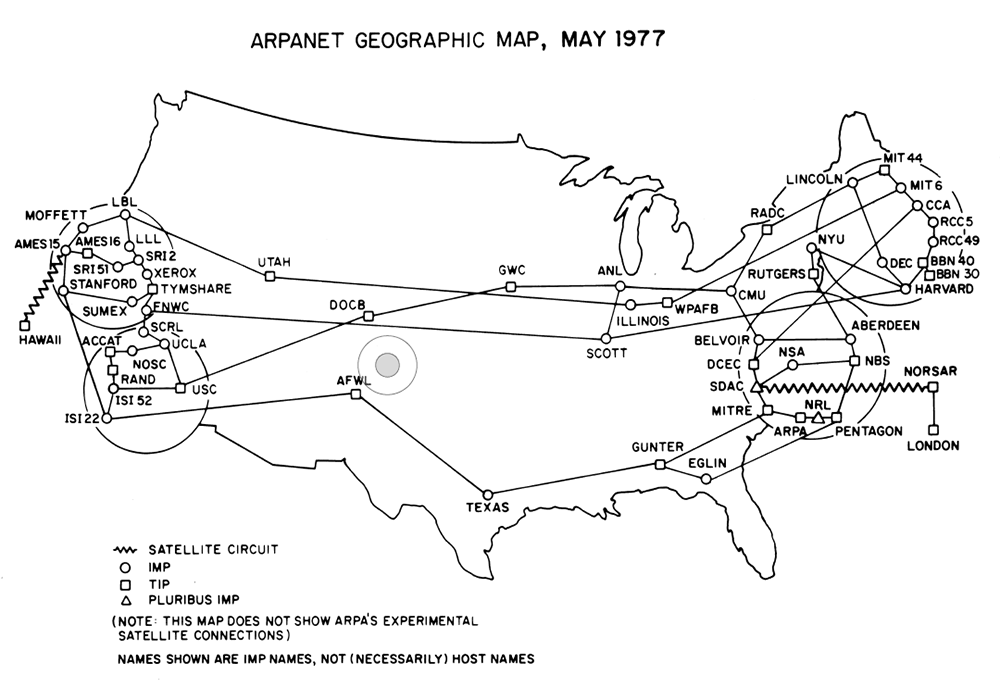
Significant expansion across U.S. military bases, government labs, and universities of ARPANET 1977.
1970s to 1980s- scale 2
The 1970s and 80s would see the first rise of commercial personal computers, as evidenced by the 1977 Trinity of Commodore, Apple, and Tandy. These computers popularized notions of home computing and decentralized access to computers. The decentralization and increased access to computers laid the groundwork for the widespread use of the internet in the years to come. From the 70s to the 80s, the US military continued experimenting with ARPANET and researching the protocol required for the stable transfer of information. The size of ARPANET continues to grow across the country, eventually becoming large enough to be considered a large entity. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) were commercialized during the 1980s, which truly started the global internet age. Networks like Usenet that allowed easy sharing of data using TCP and IP became popular and served as an early decentralized version of the Internet.
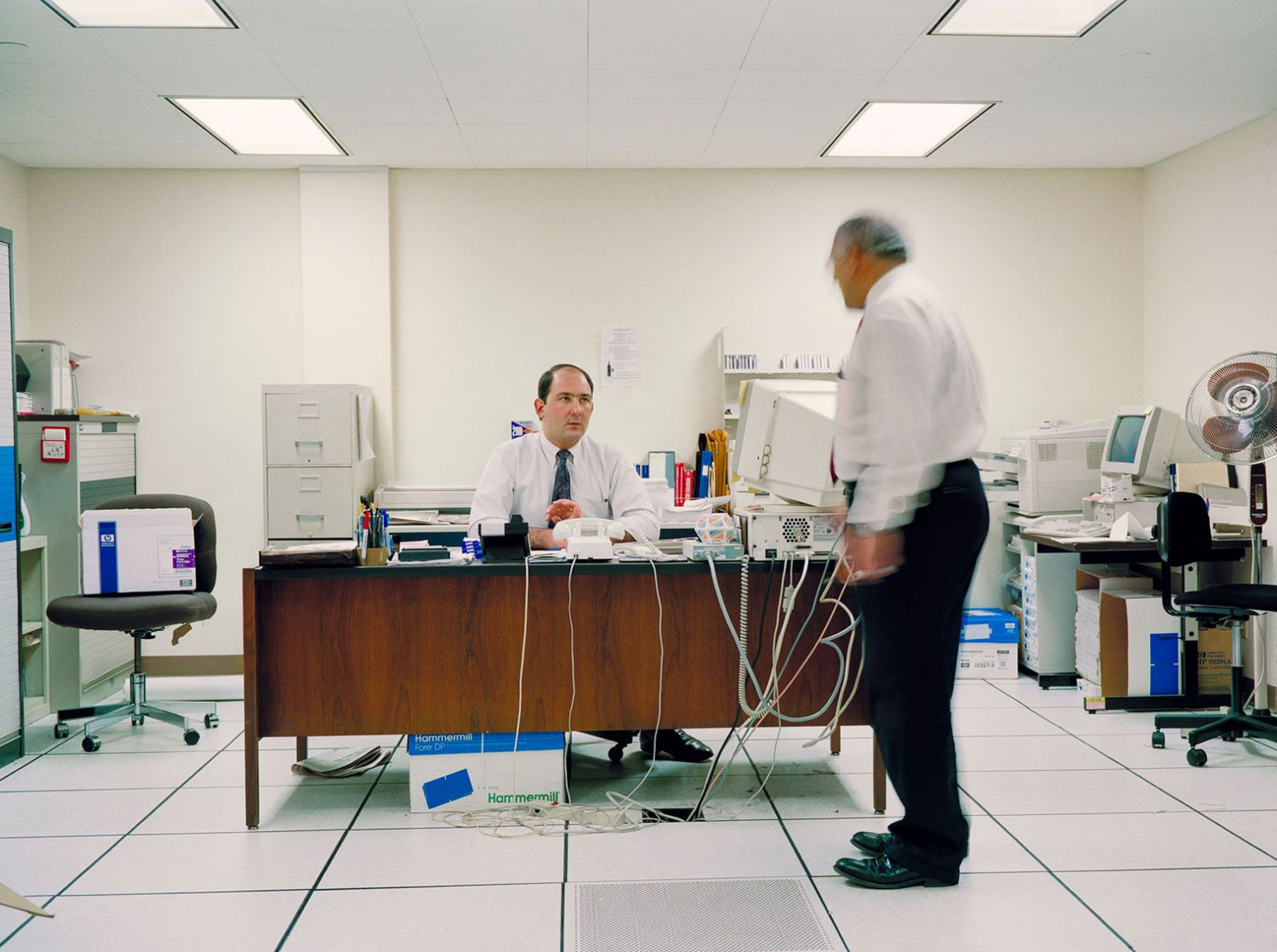
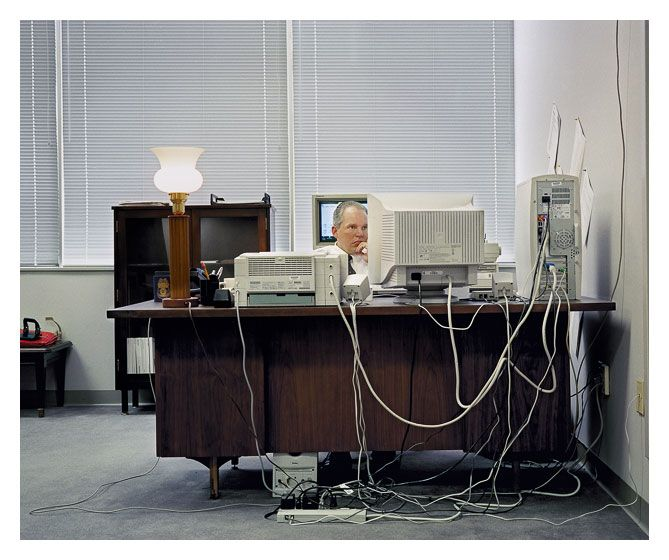
Photos of 90s Offices by Steven Ahlgren
Serial Experiments Lain is a Japanese anime television series created and co-produced by Yasuyuki Ueda, written by Chiaki J. Konaka, and directed by Ryūtarō Nakamura. The series follows Lain Iwakura, an adolescent girl in suburban Japan, and her relationship to the Wired, a global communications network similar to the internet.
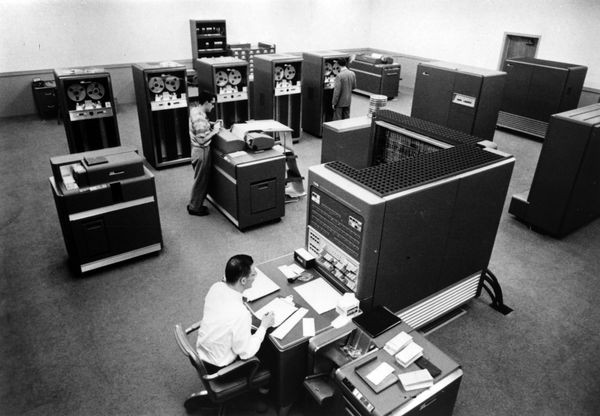
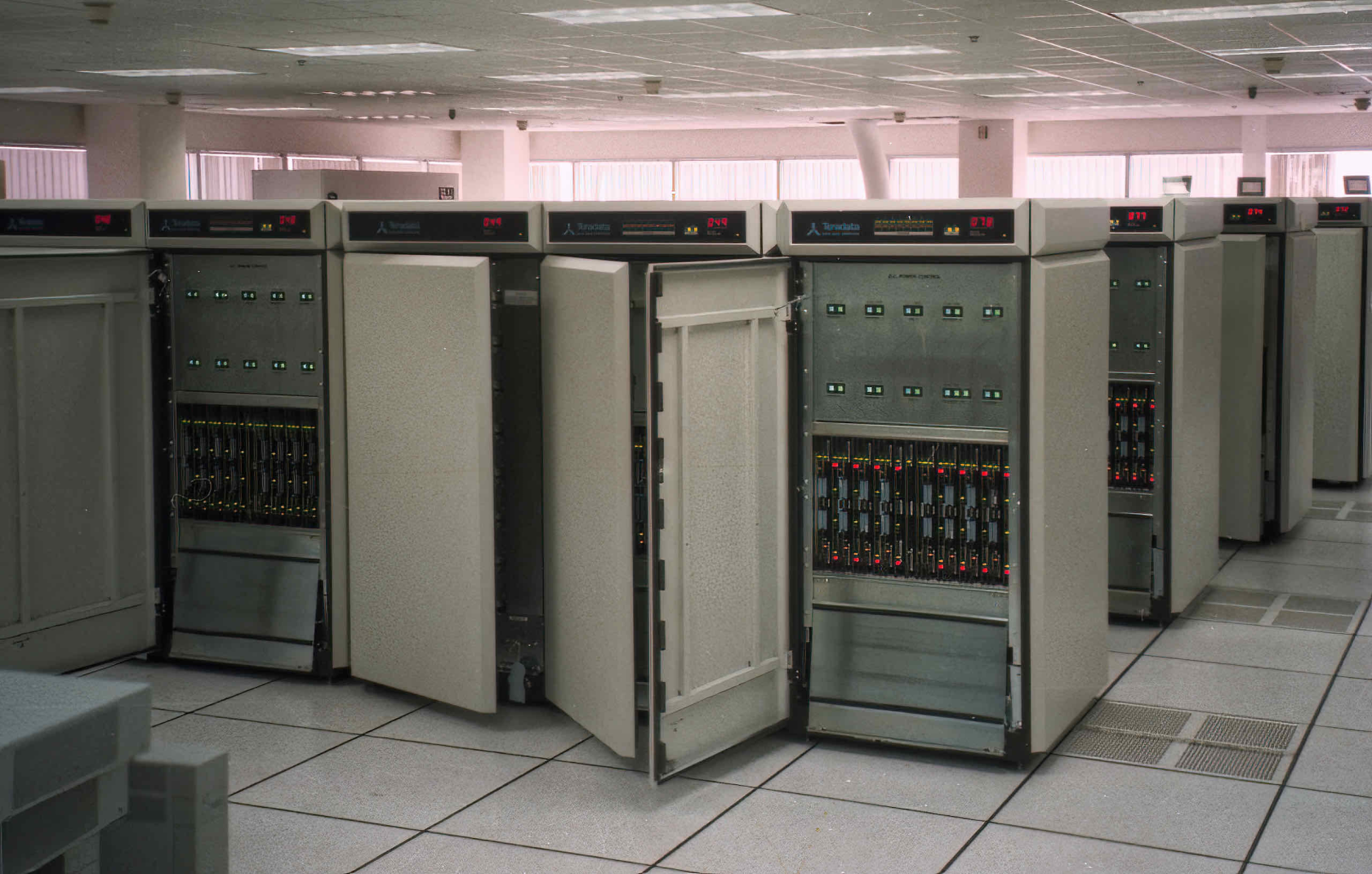
a data centre located in Los Angeles in the 1990s from Teradata
NSFNET Traffic 1991, NSFNET backbone nodes are shown at the top, regional networks below, traffic volume is depicted from purple (zero bytes) to white (100 billion bytes), visualization by NCSA using traffic data provided by the Merit Network.
1990s - scale 3
With substantial personal computers available across the country, the internet became more available as well. As the old ARPANET faded out, NSFNET came to replace the original network as a system to connect various educational and research facilities. The NSFNET would be much more relaxed in comparison to the military-driven ARPANET and allowed more users to connect and even connect to localized networks. The NSFNET paved the way to a model of internet organization, or the organization of a network of networks. The network established a hierarchical model of backbone, from regional to local. It would also firmly establish TCP/IP as a universal protocol. Through its government-funded characteristics, the network provided a framework for a public and potentially global infrastructure. Although NSFNET would be decommissioned in the 1990s, Network Service Providers as private entities arose to replace the job. Although the providers did not form a single backbone, the collective network they formed replaced the function.
NSFNET privatization and Commercial Internet providers
Web & Software Growth
Corporate IT Infrastructure
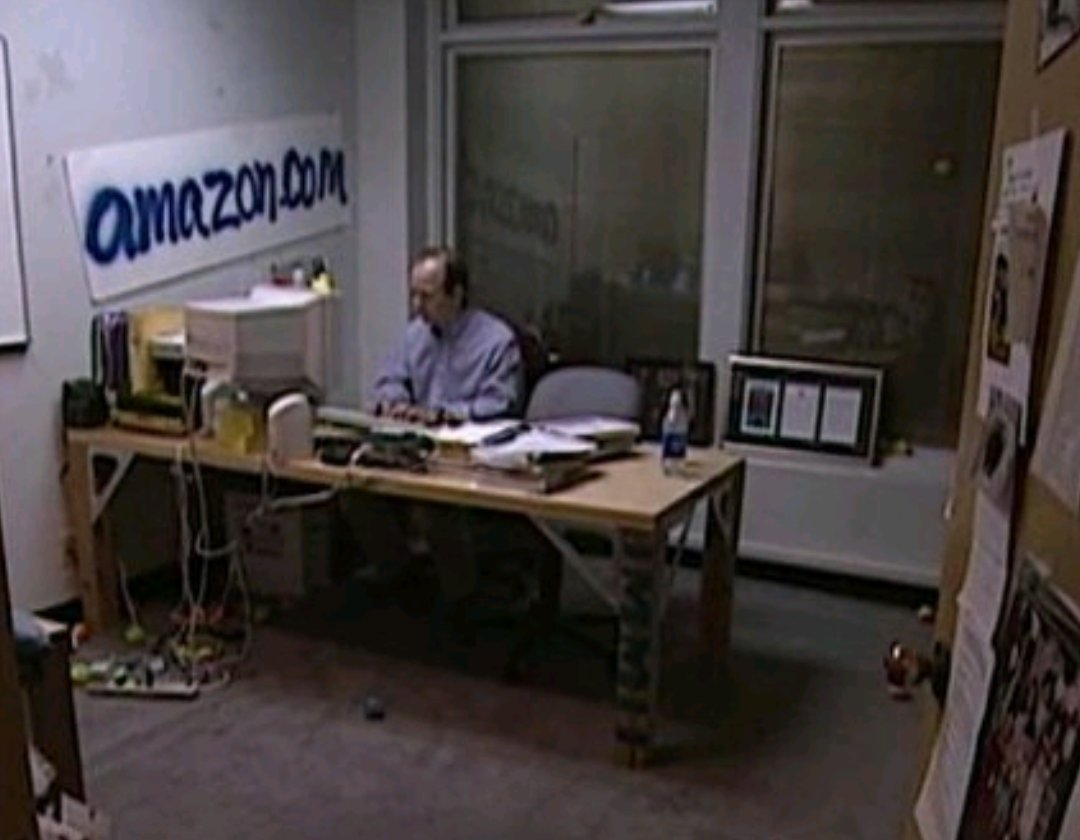
Early Amazon Office
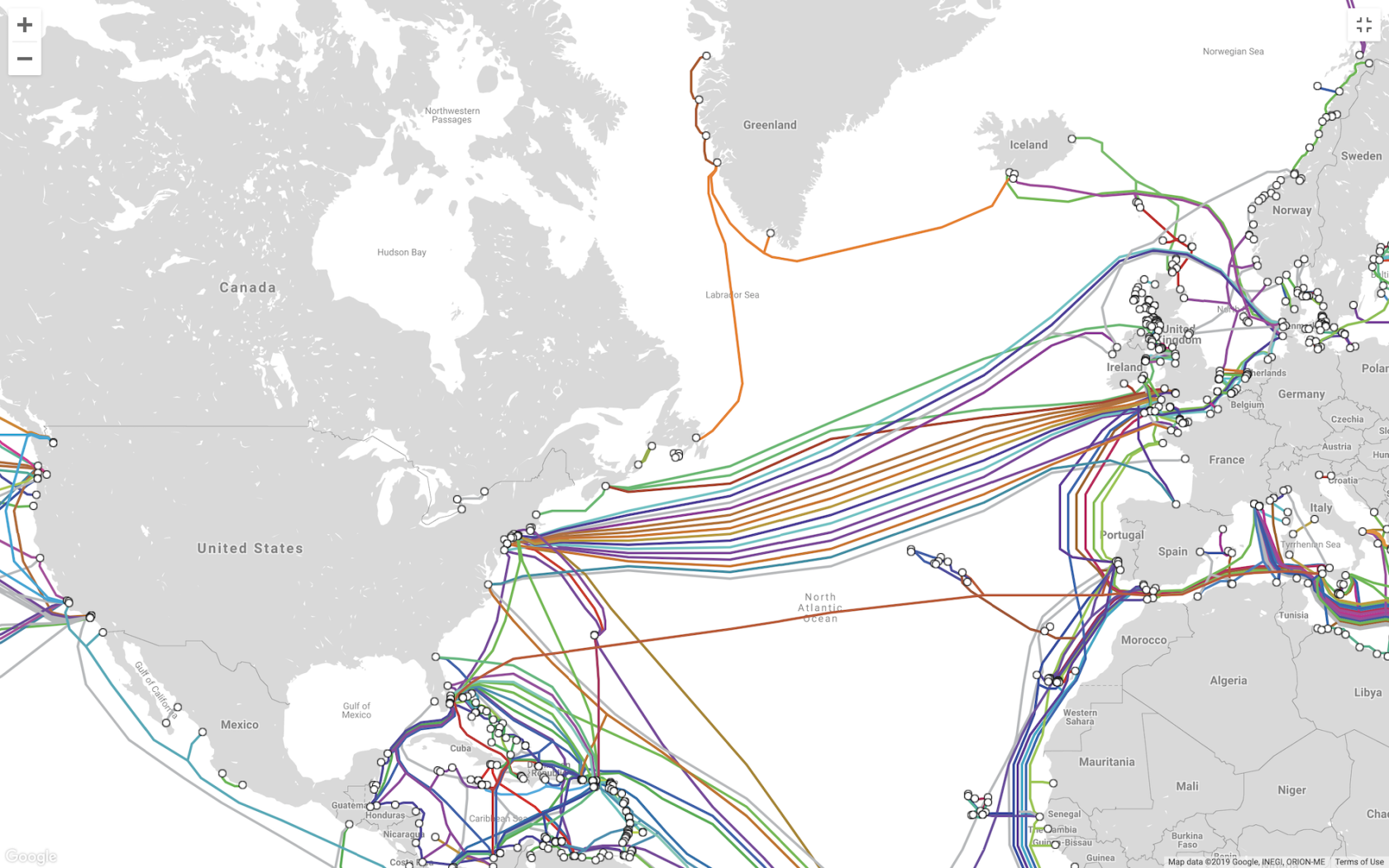
Transatlantic Internet Cables.
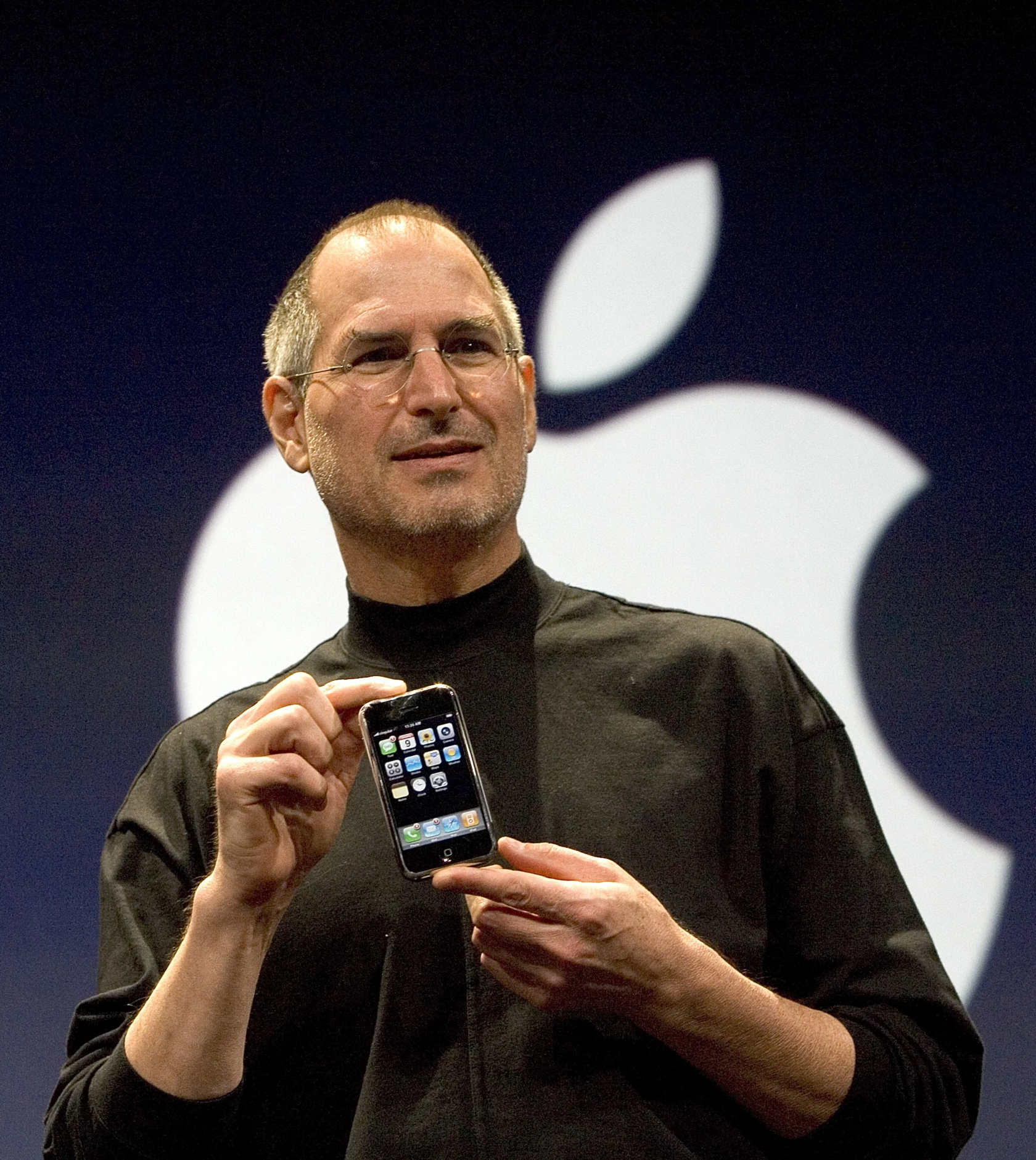
Steve Jobs releasing the iphone in 2007
2000s - scale 4
Building off from the momentum of the 1990s, the further accelerated internet with broader bandwidth allowed the internet to spread almost at the speed at which it transfers its signals. Data Centers rapidly developed to handle the large internet traffic, whether it's web services, e-commerce, or enterprise. Notion of the Cloud also developed with these data centers, with Amazon launching its AWS service in 2006, which will soon be the virtual calculation backbone of the internet. In addition to the convenience, the security of the network itself became a subject of focus in the context of global terrorist activities. One end was to build faster and more efficient internet services, but on the other hand, these services need to be surveilled as well. The release of the iPhone would also provide a gateway to the mobility revolution of the internet.
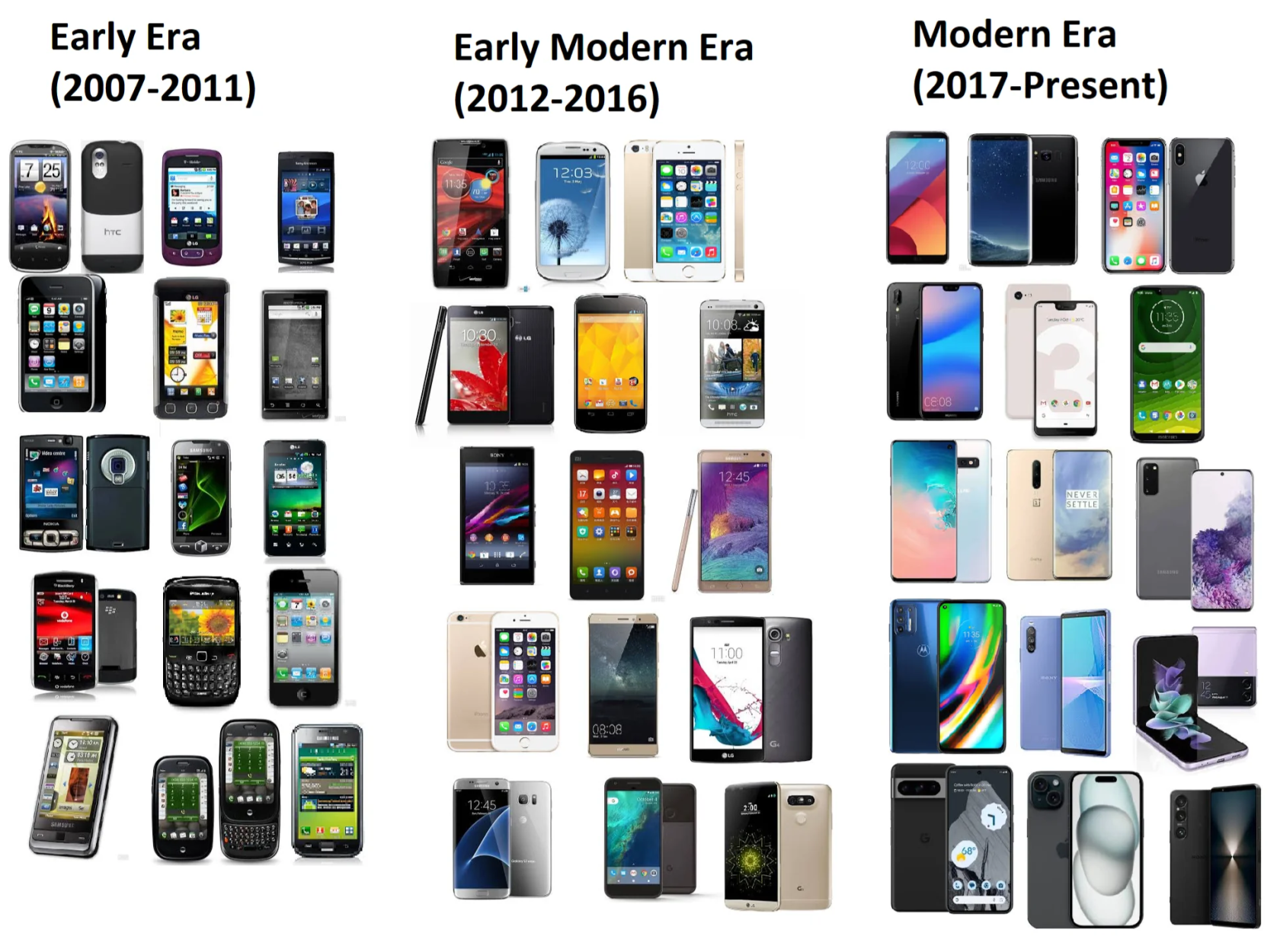
Generation of smart phones from Reddit
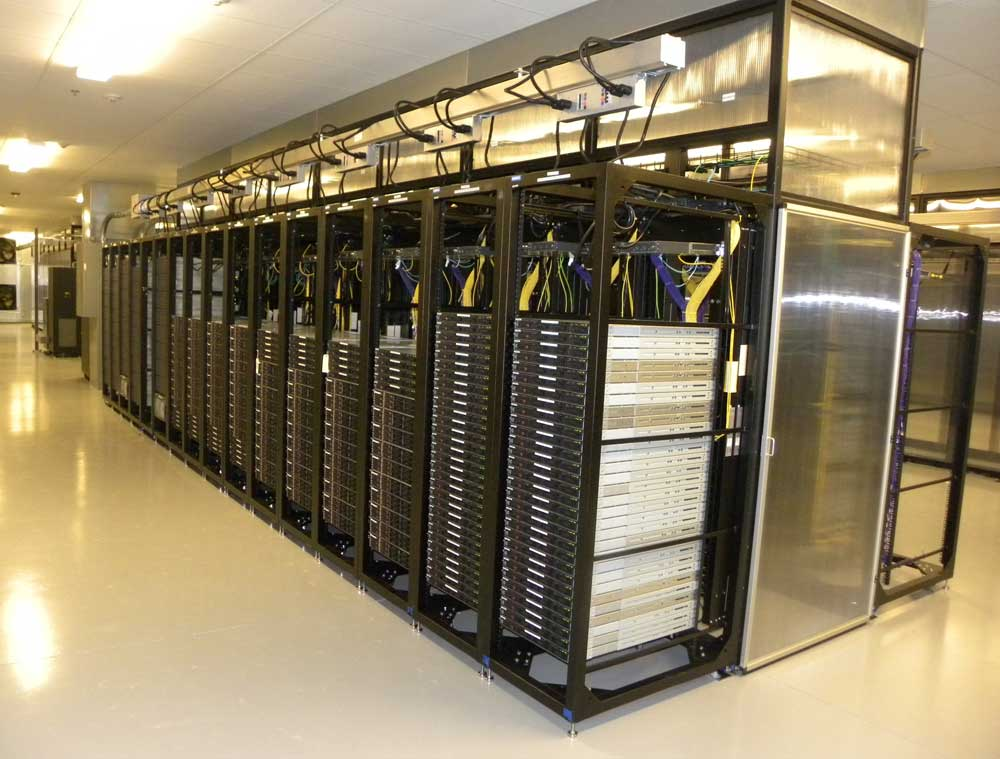
Yahoo's Servers from 2010.
2010s - Scale 5
The smartphone would further enhance the local decentralized nature of the internet. Every person now processes a miniature computer capable of accessing the internet, upscaling the internet's traffic further. The increase in traffic demands more data centers to be built. It is during this time, that the notion of the cloud fully emerged and begin to replace traditional ways of view file storage. The cloud became a vastly accessible infrastructure that can be adapted through software. To support the growth of the internet, internet infrastructure such as fiber optics and signal towers was heavily invested in by governments. At this point, the economic health of a country is simultaneously tied to the internet itself.











No comments to display
No comments to display