Internet Technologies
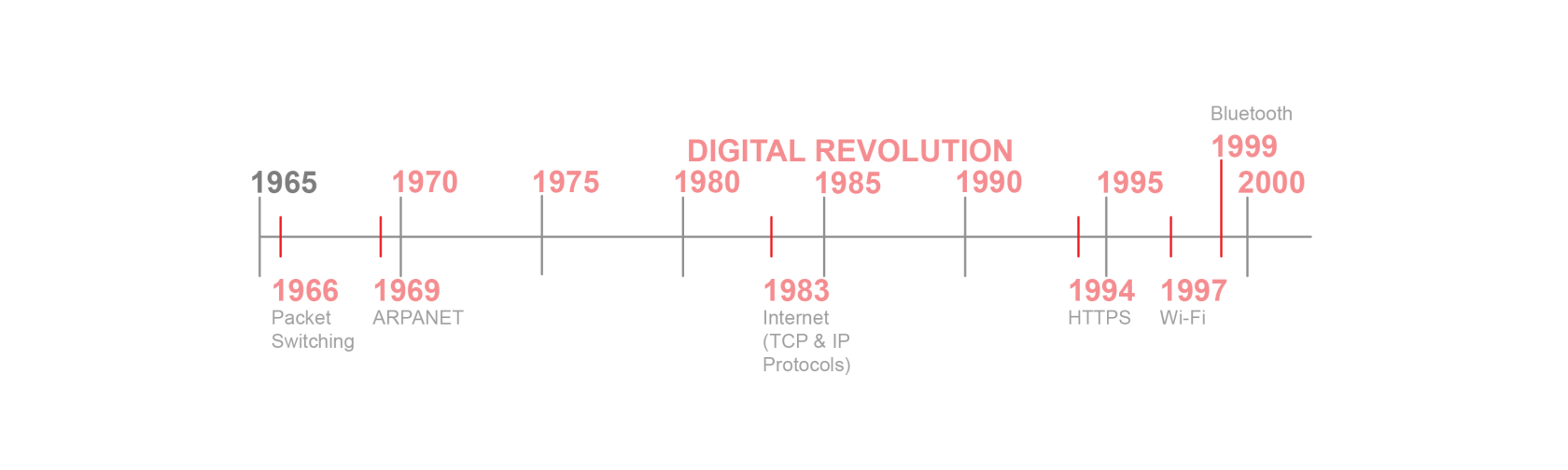
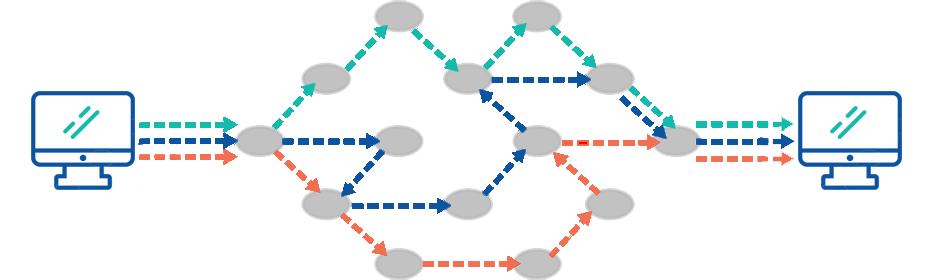
1966 - Packet Switching is the concept of breaking data into smaller parts that are then sent independently across a network. Once they arrive at the destination, the packets are reassembled. |
1969 - ARPANET is the first operational packet switching network, relying on IMPs (Interface Message Processors) as early routers. It is generally thought of to be the predecessor to the internet and built heavily on fundamental digital communication principles. It combines ideas from radio (wireless signals), satellites (long-distance communication), and cables (physical network infrastructure).
1983 - Invention of the Internet evolves from ARPANET and relies on satellites, undersea cables, and radio to transmit data globally. Turns communication from a point-to-point activity (like telegraph or telephone) into a mass, interconnected digital network.
The internet used TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) & IP (Internet Protocol).
TCP - Breaks data into packets at the source, numbers them, and ensures they arrive intact and in order at the destination. Think of it like certified mail: each packet must be signed off at delivery.
IP - Handles addressing and routing. It decides where each packet should go, using IP addresses. Think of it like writing an address on an envelope — it ensures the mail carrier knows the destination.
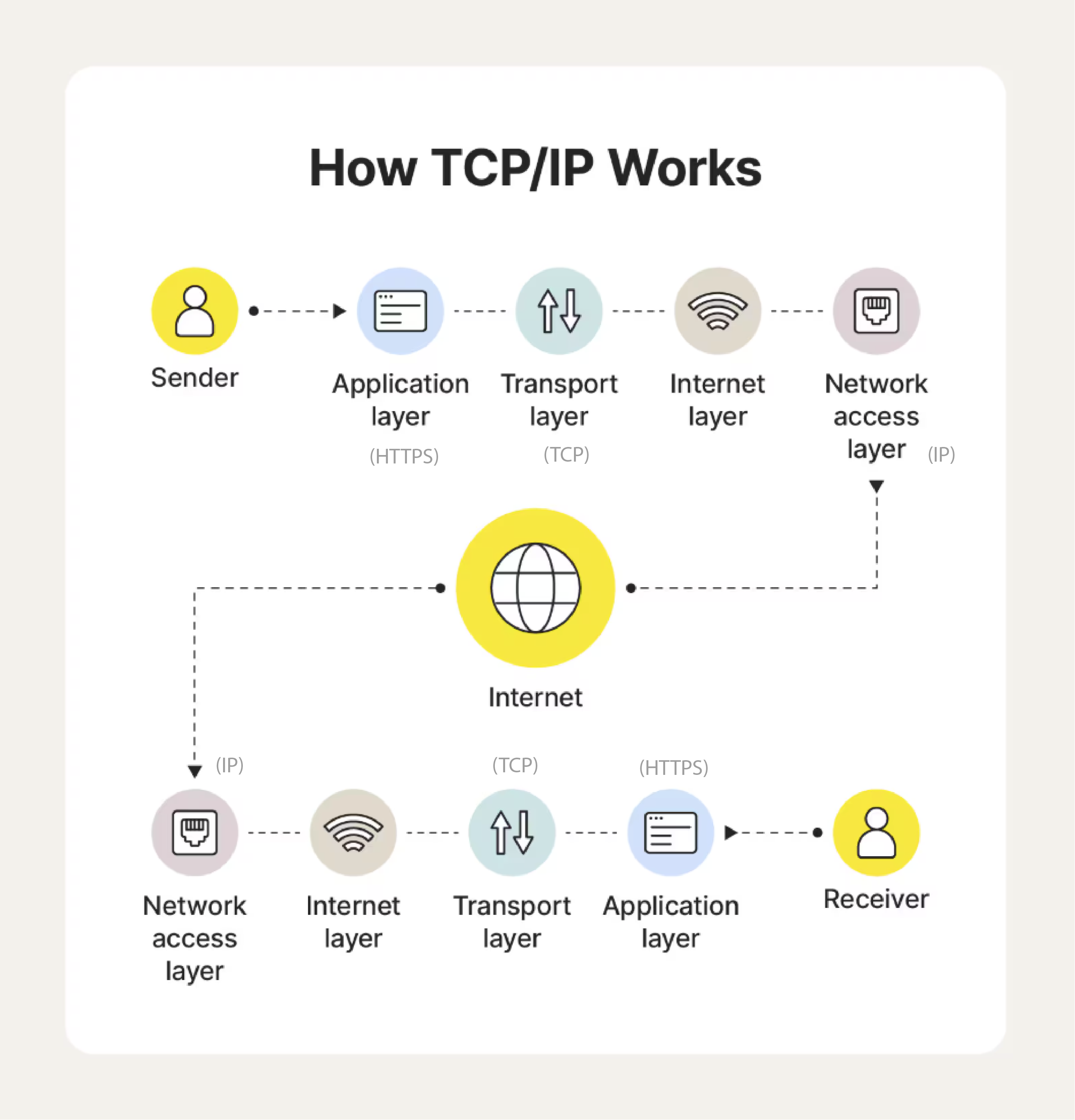
1994 - HTTPS served as a way to easily share and navigate information across the Internet. Made a a universal communication platform usable for everyone.
Consider this analogy: Internet = the global network infrastructure (roads).
HTTP = a protocol that let us build the Web on top of that network (cars that drive on the roads).
A program to view them → the first web browser/editor (called World Wide Web).
1997 - Wi-Fi is invented to convert digital data into radio waves, connecting devices to the internet without cables (wireless local area networking) It combines radio waves that transmit through the air, digital networking (ARPANET/internet), and protocol standardization (HTTP, TCP/IP) to make global internet access portable and wireless.
1999 - Bluetooth is a form of wireless communication to the personal level, extending the principles of radio and satellite to tiny devices like phones and headsets. The technology is short-range and wireless.
Conclusion: Wider, global connectivity flourished with the advent of satellites, but the internet brought virtual communication into homes and personal lives. Wireless technologies such as smartphones and Bluetooth devices were brought to the commercial market and filled the need for short-distance communication. |
No comments to display
No comments to display