Satellite & GPS
This timeline of events is prefaced by the 1896 invention of the Radio. It used electromagnetic waves to transmit signals without wires.
All wireless system we use — Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, satellite communication, GPS, and even your smartphone — is built on the principles of radio communication. However, the drawback with early radio was that it was messy, insecure, and limited in reach.
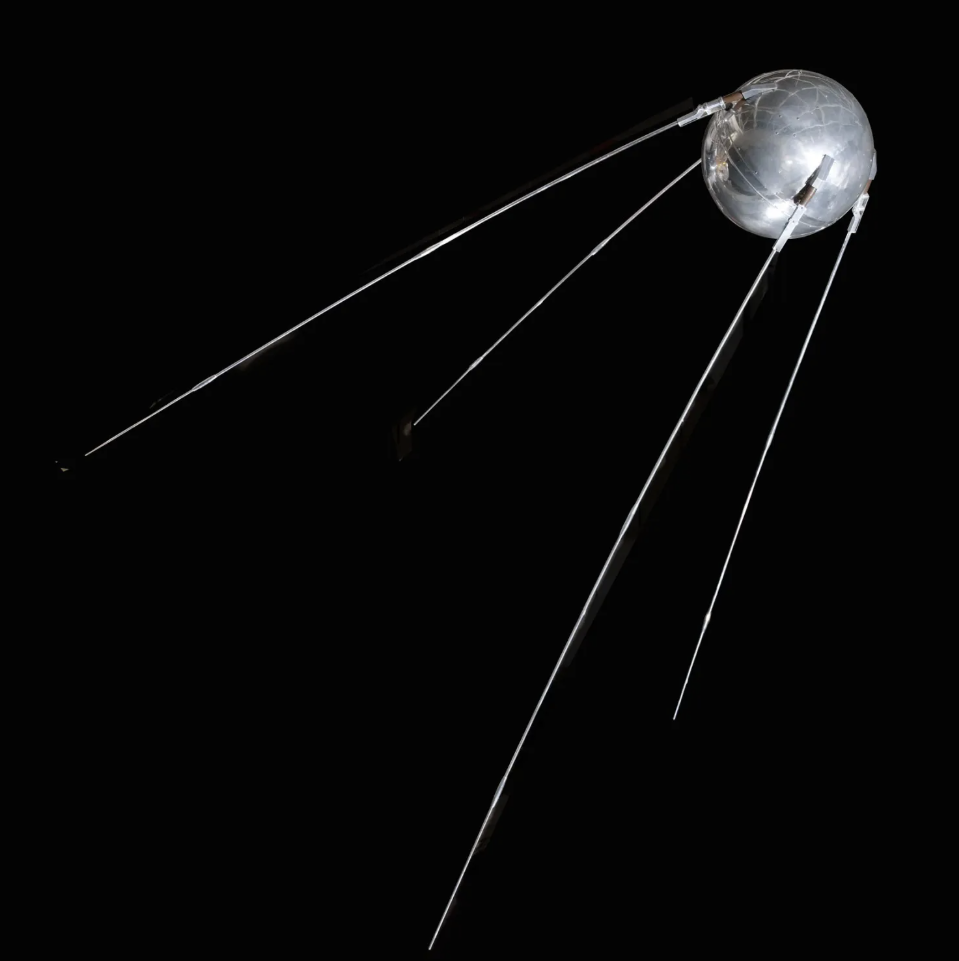
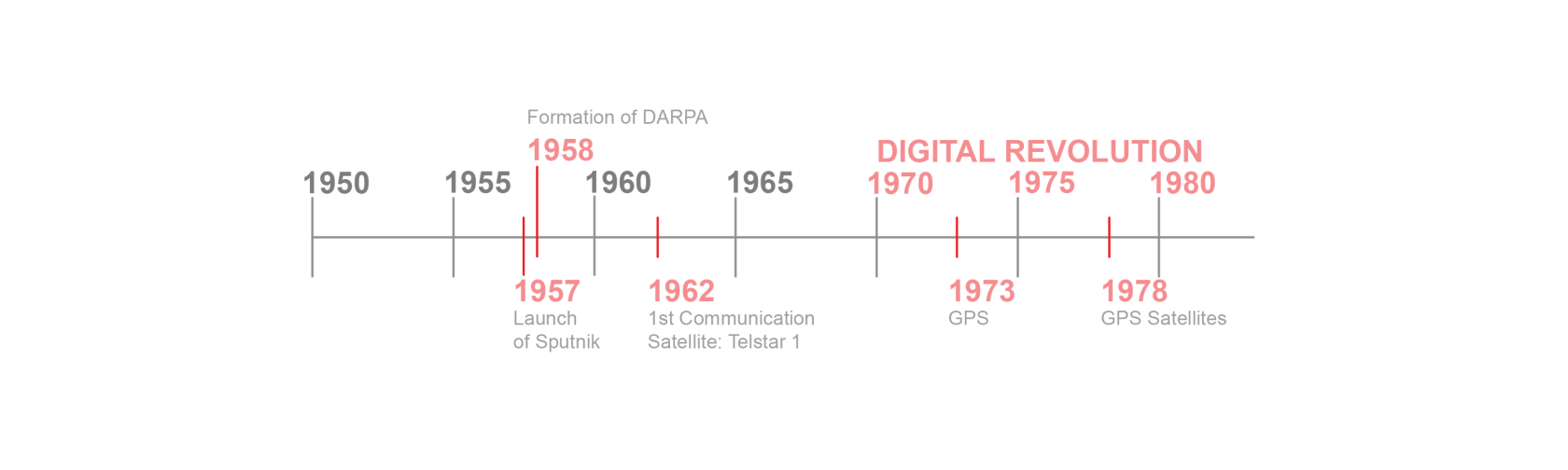
1957 - Sputnik was launched as the first satellite. The transmitted beeping radio signals that were heard worldwide accelerated the Space Race. It transmitted simple radio beeps (“beep-beep”) back to Earth. Satellites could send signals far beyond the limits of radio towers, enabling global broadcasts, telephone calls, and later internet backbones. |
1958 - DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) was founded in response to Russia's Sputnik. DARPA's mission is to "create technological surprise for US national security," leading to many risky yet rewarding projects that have revolutionized our world's technology.
1962 - Telstar 1 was the first communication satellite that relayed TV and telephone signals over the Atlantic. It directly led to the communications, weather, navigation, and scientific satellites we rely on today. 1973 - GPS was originally developed under DARPA. GPS was crucial in the Cold War as it allowed troops, ships, and aircraft to know their exact positions anywhere in the world, crucial for navigation and precise missile targeting. 1978 - First GPS satellite launched, eventually forming a global network that we use today for daily navigation. |
Conclusion: The Space Race and fast advancements in satellite technology suggest a global struggle for power post WW2. These fast pace developments in that connected the world globally serve as the backdrop for the invention of the Internet. |

No comments to display
No comments to display